| face recognition / iris scan | |
  1 in Sarai Reader 2002, 'The face of the future', p.295 Rana Dasgupta or The Face of the Future |
The field of
computer vision today is also closely connected to biometric inventions.
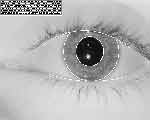
Biometric systems include face recognition, iris scan, fingerprint
analysis and other methods of characterizing biological marks for
authentification and identification. The possibility of machinic vision to recognize stored data patterns especially after 911 is thought to bring back some of the seemingly 'lost security' (if there ever was). 'Allowing your very face to be converted into a digital code that can be checked at any moment without the need for any consenting action from you (such as the swipe of a credit card), they alter the imaginery realm considerably. The possibility of being known at any point, of your identity being continually checked - in banks, shopping malls, airports etc. - against everything else that is known about you will seem like a massive escalation in the observation matrix from the more occasional 'checking-in' we currently do with each passport check or ATM withdrawal.'1 |
 |
Beneath the inherent norms, which necessarily are incorporated from the descended backgrounds and circumstances, there are obviously also the ones which socially evolved in the period and area. 'Norms are crucial to any surveillance system, for without them it cannot identify the abnormal. Norms are what enable it to decide what information should be turned into knowledge and what individuals need to be monitored. ... (The power to produce and apply norms, as Foucault tells us, is a crucial social power.) It is not hard to imagine circumstances in which political profiles of those who, by some standards, would be judged 'not normal' could be as useful to government agencies as consumer profiles are to commercial ones.'2 |
| 2 in 'The Visual Culture Reader', p.155 Fiske, John |
|
| 3 in 'Electronic culture', Hayles, Katherine, p.272 or Flickering signifier 4 'Postscript on the societies of control', Deleuze, Gilles Postscript on the societies.. 5 in 'Electronic culture', Hayles, Katherine, p.272 or Flickering signifier  |
'When bodies
are constituted as information, they can not only be sold but fundamentally
reconstituted in response to market pressures'3,
today this corresponds to the logic of access in any aspect (access
to data, information, space, country, ...). Already Deleuze claimed that the numerical language of control is made of chiffre, which marks the access for information, or respectively the disallowance.4 And K.Hayles states that 'with information, the constraining factor separating the haves from the have-nots is not so much possession as access. The shift of emphasis from ownership to access is another manifestation of the underlying transition from presence/absence to pattern/ randomness.'5 |
| By any means
the problem of access to programming these devices or the fact who
is interpreting the perceived images is equally important to visibility
/ invisibility, as to the thereby constituted evidence. As this is the point where norms are established. |
|
 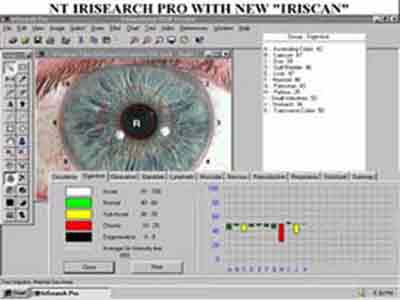 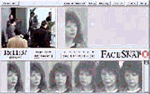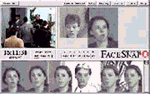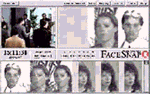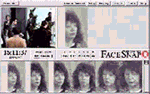 |
On the other side there is also evidence that this devices do not work that properly and can be faked or manipulated very easily: Japanese researcher gums up biometrics scanners Robo Cop A text about the change in surveillance after 911 from David Lyon Surveillance: After September 11, 2001 another text by David Lyon Surveillance in Information Societies: Before and After September 11 2001 There is much more on surveillance on sarai reader sarai 02 more about the technics and industries: Iris Recognition and more machine vision facesnap and information about biometrics in german at Passwort Mensch and Streitfall Biometrie |